Enabling longer delivery fibers with the RSS
On: Oct 05, 2021
In: High Power Lasers
Fiber laser metal cutting machines with fiber-based beam delivery must have a delivery fiber long enough to access all targeted locations on the workpiece.
Learn more about the benefits of Raman Scattering Suppressor (RSS) to enable longer fibers in high throughput multi-kW cutting systems.
Stimulated Raman Scattering: A major challenge for industrial fiber laser designers
With the growing trend of increasing throughput in fiber laser cutting machines, laser design challenges arise for faster cutting of larger and thicker workpieces. How is it possible to deliver more power over longer distances without compromising too much on the beam quality? One problem is the management of Stimulated Raman Scattering (SRS), which is exacerbated when high optical power travels through long fibers.
SRS is a well-known limitation to the power scaling of fiber lasers for material processing applications; it has detrimental effects on laser efficiency, stability, and reliability. SRS grows exponentially when the laser output power exceeds a certain level, also known as the SRS threshold, which depends on the laser design and use cases.
SRS photons can be generated at multiple locations of the optical chain and typically build up along the chain, including in the delivery fiber. SRS can destabilize the laser emission, hampering the metal cutting process's stability and reliability. In the worst case, some components of the fiber laser module will be damaged.
Killing SRS at the source with Fiber Bragg Gratings
Several strategies exist to increase the SRS threshold in high-power laser systems; however, these strategies often involve trade-offs in beam quality or other laser performance levels. They also compromize the mitigation of other power scaling limitations, such as Transverse Mode Instability (TMI) [1]. The most effective way to deal with SRS is to prevent its build-up, especially when long fibers are to be used. This was the mindset of TeraXion engineers when they developed the RSS.
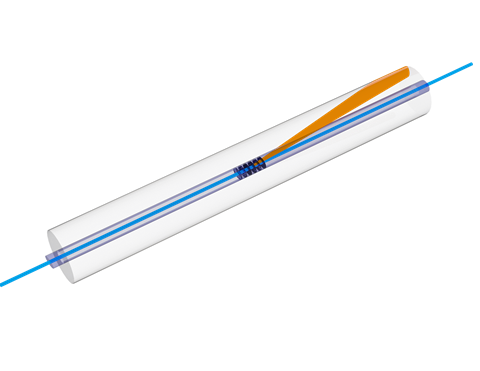
TeraXion’s RSS kills SRS at the source using patented Chirped Tilted Fiber Bragg Grating (CTFBG) technology [2] which blocks SRS photons and redirects them into the cladding of the fiber (Figure 1), where they can be absorbed using a cladding mode stripper (CMS), which is typically present at the output of the fiber laser cavity.
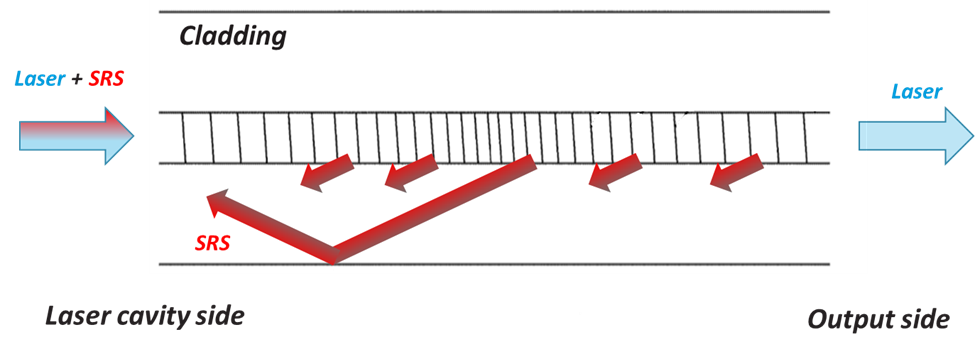
Figure 1. Illustration of the operating principle of RSS based on TeraXion’s patented CTFBG technology.
By inserting RSS right after the CMS, SRS is removed before it enters the delivery fiber, thereby limiting additional SRS accumulation in the latter. As a result, longer delivery fibers can be used in laser cutting systems with higher power levels and smaller core diameters.
The effectiveness of the RSS in enabling long delivery fibers will become evident by examining the results obtained with the configuration shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2. Schematic representation of the experimental configuration.
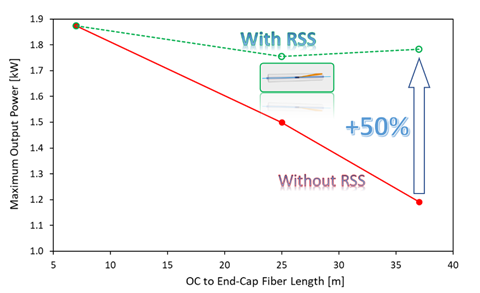
Different lengths of delivery fiber (20/400) were added to the output of a fiber laser oscillator. The output power of the laser was increased until the onset of instabilities due to SRS was observed. The experiment was performed with and without RSS inserted after the CMS in order to compare the maximum safe output power levels that can be achieved in both cases. The results are shown in Figure 3.
Figure 3. Maximum achievable output power as a function of fiber length downstream of the OC, with and without RSS.
The RSS allowed for maintaining the output power at a nearly constant maximum value for fiber lengths up to 37 meters downstream of the laser cavity, which is up to 50% more powerful than without RSS. Due to the nonlinear nature of SRS, this difference and, therefore, the benefits of the RSS are expected to grow with the output power.
Conclusion
In short, if you are looking for solutions to design multi-kW fiber lasers with long delivery cables for high throughput laser metal cutting applications, considering RSS in your toolbox is definitely a smart decision. Not only will you be able to deliver outstanding performances to your customers, but you will also be able to grab their attention by offering them a rock-solid laser with consistent cutting results over thousands of hours.
For more information
For questions, specific requirements or to learn more about TeraXion’s products, contact us at info@teraxion.com
[1] P. Deladurantaye, SRS remains a major development challenge for multikilowatt fiber lasers used in industrial applications, Laser Focus World, May 2021, pp. 42-22
[2] Patents granted: US10393955 and US10663654. Patents pending: US20200333529 and CA2971601
Related Topics